Overview¶
Note
this section is a technical overview of the internal API of Alembic. This section is only useful for developers who wish to extend the capabilities of Alembic; for regular users, reading this section is not necessary.
A visualization of the primary features of Alembic’s internals is presented in the following figure. The module and class boxes do not list out all the operations provided by each unit; only a small set of representative elements intended to convey the primary purpose of each system.
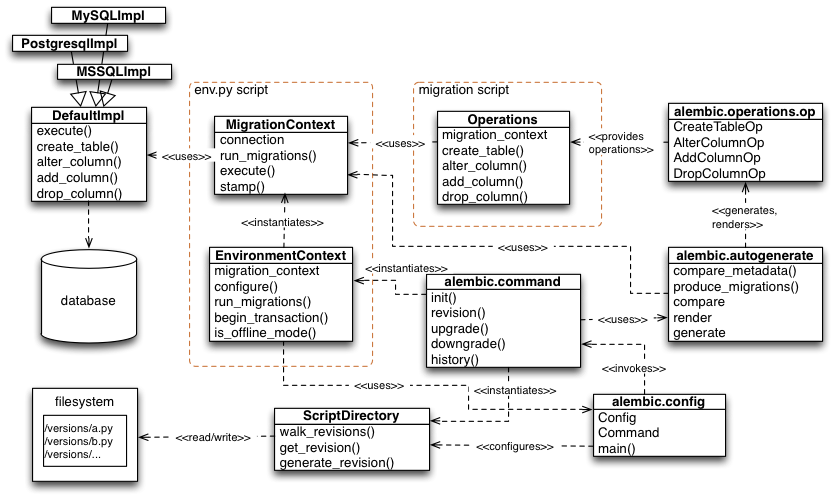
The script runner for Alembic is present in the Configuration module.
This module produces a Config object and passes it to the
appropriate function in Commands. Functions within
Commands will typically instantiate an
ScriptDirectory instance, which represents the collection of
version files, and an EnvironmentContext, which is a configurational
facade passed to the environment’s env.py script.
The EnvironmentContext object is the primary object used within
the env.py script, whose main purpose is that of a facade for creating and using
a MigrationContext object, which is the actual migration engine
that refers to a database implementation. The primary method called
on this object within an env.py script is the
EnvironmentContext.configure() method, which sets up the
MigrationContext with database connectivity and behavioral
configuration. It also supplies methods for transaction demarcation and
migration running, but these methods ultimately call upon the
MigrationContext that’s been configured.
MigrationContext is the gateway to the database
for other parts of the application, and produces a DefaultImpl
object which does the actual database communication, and knows how to
create the specific SQL text of the various DDL directives such as
ALTER TABLE; DefaultImpl has subclasses that are per-database-backend.
In “offline” mode (e.g. --sql), the MigrationContext will
produce SQL to a file output stream instead of a database.
During an upgrade or downgrade operation, a specific series of migration
scripts are invoked starting with the MigrationContext in conjunction
with the ScriptDirectory; the actual scripts themselves make use
of the Operations object, which provide the end-user interface to
specific database operations. The Operations object is generated
based on a series of “operation directive” objects that are user-extensible,
and start out in the Built-in Operation Objects module.
Another prominent feature of Alembic is the “autogenerate” feature, which
produces new migration scripts that contain Python code. The autogenerate
feature starts in Autogeneration, and is used exclusively
by the alembic.command.revision() command when the --autogenerate
flag is passed. Autogenerate refers to the MigrationContext
and DefaultImpl in order to access database connectivity and
access per-backend rules for autogenerate comparisons. It also makes use
of Built-in Operation Objects in order to represent the operations that
it will render into scripts.