概述¶
Overview
SQLAlchemy SQL 工具包和对象关系映射器 是一套用于与数据库和 Python 一起工作的全面工具。它有多个独立的功能区域,可以单独使用或组合使用。其主要组件如下图所示,组件依赖关系按层次组织:
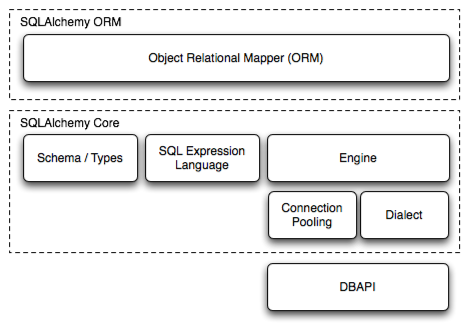
上图中,SQLAlchemy 最重要的两个前端部分是 对象关系映射器 (ORM) 和 核心 (Core)。
核心包含了 SQLAlchemy 的 SQL 和数据库集成与描述服务的广度,其中最突出的部分是 SQL 表达式语言 。
SQL 表达式语言本身就是一个独立于 ORM 包的工具包,它提供了一种构建由可组合对象表示的 SQL 表达式的系统,这些表达式可以在特定事务的范围内“执行”,并返回结果集。插入、更新和删除(即:术语 DML)是通过传递表示这些语句的 SQL 表达式对象以及表示每个语句的参数的字典来实现的。
ORM 构建在核心之上,提供了一种将领域对象模型映射到数据库模式的工作方式。使用 ORM 时,SQL 语句的构建方式与使用核心时大致相同,但 DML 任务,即在数据库中持久化业务对象的任务,是使用称为 工作单元 (unit of work) 的模式来自动化的,该模式将可变对象的状态变化转换为 INSERT、UPDATE 和 DELETE 构造,然后以这些对象的术语调用它们。SELECT 语句也通过 ORM 特定的自动化和面向对象的查询功能得到了增强。
虽然使用核心和 SQL 表达式语言呈现的是数据库的模式中心视图,编程范式围绕着不可变性,但 ORM 在此基础上构建了数据库的领域中心视图,其编程范式更明确地面向对象并依赖于可变性。由于关系数据库本身就是一个可变服务,不同之处在于核心/SQL 表达式语言是面向命令的,而 ORM 是面向状态的。
The SQLAlchemy SQL Toolkit and Object Relational Mapper is a comprehensive set of tools for working with databases and Python. It has several distinct areas of functionality which can be used individually or combined together. Its major components are illustrated below, with component dependencies organized into layers:

Above, the two most significant front-facing portions of SQLAlchemy are the Object Relational Mapper (ORM) and the Core.
Core contains the breadth of SQLAlchemy’s SQL and database integration and description services, the most prominent part of this being the SQL Expression Language.
The SQL Expression Language is a toolkit on its own, independent of the ORM package, which provides a system of constructing SQL expressions represented by composable objects, which can then be “executed” against a target database within the scope of a specific transaction, returning a result set. Inserts, updates and deletes (i.e. DML) are achieved by passing SQL expression objects representing these statements along with dictionaries that represent parameters to be used with each statement.
The ORM builds upon Core to provide a means of working with a domain object model mapped to a database schema. When using the ORM, SQL statements are constructed in mostly the same way as when using Core, however the task of DML, which here refers to the persistence of business objects in a database, is automated using a pattern called unit of work, which translates changes in state against mutable objects into INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE constructs which are then invoked in terms of those objects. SELECT statements are also augmented by ORM-specific automations and object-centric querying capabilities.
Whereas working with Core and the SQL Expression language presents a schema-centric view of the database, along with a programming paradigm that is oriented around immutability, the ORM builds on top of this a domain-centric view of the database with a programming paradigm that is more explicitly object-oriented and reliant upon mutability. Since a relational database is itself a mutable service, the difference is that Core/SQL Expression language is command oriented whereas the ORM is state oriented.
文档概述¶
Documentation Overview
文档分为四个部分:
SQLAlchemy 统一教程 - 这个全新的 1.4/2.0/2.1 系列的 SQLAlchemy 教程 以整体的方式介绍了整个库,从核心的描述开始,逐步介绍了更多面向 ORM 的概念。 新用户,以及从 1.x 系列迁移过来的用户,应从这里开始。
SQLAlchemy ORM - 在本节中,展示了 ORM 的参考文档。
SQLAlchemy Core - 在这里,展示了核心中所有其他内容的参考文档。还描述了 SQLAlchemy 引擎、连接和池服务。
The documentation is separated into four sections:
SQLAlchemy 统一教程 - this all-new tutorial for the 1.4/2.0/2.1 series of SQLAlchemy introduces the entire library holistically, starting from a description of Core and working more and more towards ORM-specific concepts. New users, as well as users coming from the 1.x series of SQLAlchemy, should start here.
SQLAlchemy ORM - In this section, reference documentation for the ORM is presented.
SQLAlchemy Core - Here, reference documentation for everything else within Core is presented. SQLAlchemy engine, connection, and pooling services are also described here.
Dialects - Provides reference documentation for all dialect implementations, including DBAPI specifics.
代码示例¶
Code Examples
工作代码示例,主要涉及 ORM,包含在 SQLAlchemy 发行版中。所有包含的示例应用程序的描述在 核心和 ORM 示例。
在 wiki 上还提供了各种涉及核心 SQLAlchemy 构造和 ORM 的示例。请参阅 Theatrum Chemicum。
Working code examples, mostly regarding the ORM, are included in the SQLAlchemy distribution. A description of all the included example applications is at 核心和 ORM 示例.
There is also a wide variety of examples involving both core SQLAlchemy constructs as well as the ORM on the wiki. See Theatrum Chemicum.
安装指南¶
Installation Guide
支持的平台¶
Supported Platforms
支持的安装方法¶
Supported Installation Methods
SQLAlchemy 的安装通过基于 setuptools 的标准 Python 方法,
可以直接引用 setup.py 或使用 pip 或其他兼容 setuptools 的方法进行安装。
SQLAlchemy installation is via standard Python methodologies that are
based on setuptools, either
by referring to setup.py directly or by using
pip or other setuptools-compatible
approaches.
通过 pip 安装¶
Install via pip
当 pip 可用时,可以从 PyPI 下载发行版并一步安装:
pip install sqlalchemy此命令将从 Python Cheese Shop 下载最新的**已发布**版本的 SQLAlchemy 并安装到您的系统中。对于大多数常见平台,将下载一个 Python Wheel 文件,该文件提供预构建的本机 Cython / C 扩展。
为了安装最新的**预发布**版本,例如 2.0.0b1,pip 需要使用 --pre 标志:
pip install --pre sqlalchemy如上所述,如果最新版本是预发布版本,它将被安装,而不是最新的已发布版本。
When pip is available, the distribution can be
downloaded from PyPI and installed in one step:
pip install sqlalchemyThis command will download the latest released version of SQLAlchemy from the Python Cheese Shop and install it to your system. For most common platforms, a Python Wheel file will be downloaded which provides native Cython / C extensions prebuilt.
In order to install the latest prerelease version, such as 2.0.0b1,
pip requires that the --pre flag be used:
pip install --pre sqlalchemyWhere above, if the most recent version is a prerelease, it will be installed instead of the latest released version.
使用 AsyncIO 支持进行安装¶
Installing with AsyncIO Support
SQLAlchemy 的 asyncio 支持依赖于 greenlet 项目。这个依赖默认不包括在内。要安装带有 asyncio 支持的 SQLAlchemy,请运行以下命令:
pip install sqlalchemy[asyncio]此安装将包括 greenlet 依赖项。有关确保 asyncio 支持存在的更多详细信息,请参阅 Asyncio 平台安装说明 部分。
在 2.1 版本发生变更: SQLAlchemy 默认不再安装 “greenlet” 依赖项;使用 sqlalchemy[asyncio] pip 目标进行安装。
SQLAlchemy’s asyncio support depends upon the
greenlet project. This dependency
is not included by default. To install with asyncio support, run this command:
pip install sqlalchemy[asyncio]This installation will include the greenlet dependency in the installation. See the section Asyncio 平台安装说明 for additional details on ensuring asyncio support is present.
在 2.1 版本发生变更: SQLAlchemy no longer installs the “greenlet” dependency by default; use the sqlalchemy[asyncio] pip target to install.
从源分发手动安装¶
Installing manually from the source distribution
如果不通过 pip 安装,可以使用 setup.py 脚本安装源代码发行版:
python setup.py install源代码安装与平台无关,无论是否安装了 Cython / C 构建工具,都可以在任何平台上安装。正如下一节 构建 Cython 扩展 详细说明的那样, setup.py 将尽可能尝试使用 Cython / C 进行构建,但如果不可能,则会退回到纯 Python 安装。
When not installing from pip, the source distribution may be installed
using the setup.py script:
python setup.py installThe source install is platform agnostic and will install on any platform
regardless of whether or not Cython / C build tools are installed. As the next
section 构建 Cython 扩展 details, setup.py will attempt to build using
Cython / C if possible but will fall back to a pure Python installation
otherwise.
构建 Cython 扩展¶
Building the Cython Extensions
SQLAlchemy 包含 Cython 扩展,这些扩展在各个领域提供了额外的速度提升,当前重点是提高核心结果集的速度。
在 2.0 版本发生变更: SQLAlchemy 的 C 扩展已使用 Cython 重写。
setup.py 将在检测到适当的平台时自动构建扩展,前提是安装了 Cython 包。完全的手动构建如下所示:
# 进入 SQLAlchemy 源代码发行版目录
cd path/to/sqlalchemy
# 安装 cython
pip install cython
# 可选地提前构建 Cython 扩展
python setup.py build_ext
# 运行安装
python setup.py install源代码构建也可以使用 PEP 517 技术进行,例如使用 build:
# 进入 SQLAlchemy 源代码发行版目录
cd path/to/sqlalchemy
# 安装 build
pip install build
# 构建源代码 / wheel 分发包
python -m build如果由于未安装 Cython、缺少编译器或其他问题导致 Cython 扩展的构建失败,设置过程将输出警告信息,并在完成后重新运行构建而不包含 Cython 扩展,并报告最终状态。
要在构建/安装过程中甚至不尝试编译 Cython 扩展,可以指定 DISABLE_SQLALCHEMY_CEXT 环境变量。其使用场景包括特殊测试情况,或者在通常的“重建”机制无法克服的兼容性/构建问题的罕见情况下:
export DISABLE_SQLALCHEMY_CEXT=1; python setup.py installSQLAlchemy includes Cython extensions which provide an extra speed boost within various areas, with a current emphasis on the speed of Core result sets.
在 2.0 版本发生变更: The SQLAlchemy C extensions have been rewritten using Cython.
setup.py will automatically build the extensions if an appropriate platform
is detected, assuming the Cython package is installed. A complete manual
build looks like:
# cd into SQLAlchemy source distribution
cd path/to/sqlalchemy
# install cython
pip install cython
# optionally build Cython extensions ahead of install
python setup.py build_ext
# run the install
python setup.py installSource builds may also be performed using PEP 517 techniques, such as using build:
# cd into SQLAlchemy source distribution
cd path/to/sqlalchemy
# install build
pip install build
# build source / wheel dists
python -m buildIf the build of the Cython extensions fails due to Cython not being installed, a missing compiler or other issue, the setup process will output a warning message and re-run the build without the Cython extensions upon completion, reporting final status.
To run the build/install without even attempting to compile the Cython
extensions, the DISABLE_SQLALCHEMY_CEXT environment variable may be
specified. The use case for this is either for special testing circumstances,
or in the rare case of compatibility/build issues not overcome by the usual
“rebuild” mechanism:
export DISABLE_SQLALCHEMY_CEXT=1; python setup.py install安装数据库 API¶
Installing a Database API
检查已安装的 SQLAlchemy 版本¶
Checking the Installed SQLAlchemy Version
本文档涵盖 SQLAlchemy 2.1 版。如果您正在使用已安装 SQLAlchemy 的系统,请从 Python 提示符检查版本,如下所示:
>>> import sqlalchemy
>>> sqlalchemy.__version__
2.1.0This documentation covers SQLAlchemy version 2.1. If you’re working on a system that already has SQLAlchemy installed, check the version from your Python prompt like this:
>>> import sqlalchemy
>>> sqlalchemy.__version__
2.1.0后续步骤¶
Next Steps
安装 SQLAlchemy 后,新老用户都可以 继续 SQLAlchemy 教程。
With SQLAlchemy installed, new and old users alike can Proceed to the SQLAlchemy Tutorial.
2.0 到 2.1 迁移¶
2.0 to 2.1 Migration
从 SQLAlchemy 2.0 版本来的用户将想要阅读:
SQLAlchemy 2.1 有什么新功能? - 2.1 版的新功能和行为
从 SQLAlchemy 1.x 版本(如 1.4 版)过渡的用户应首先过渡到 2.0 版,然后再进行从 2.0 到 2.1 的小幅过渡。1.x 到 2.x 过渡的关键文档:
迁移到 SQLAlchemy 2.0 - 从 1.3 或 1.4 迁移到 2.0 的完整背景信息
SQLAlchemy 2.0 有什么新功能? - 除 1.x 迁移外,2.0 的新功能和行为
所有变更日志和迁移文档的索引在:
Changelog catalog - 所有 SQLAlchemy 版本的详细变更日志
Users coming SQLAlchemy version 2.0 will want to read:
What’s New in SQLAlchemy 2.1? - New features and behaviors in version 2.1
Users transitioning from 1.x versions of SQLAlchemy, such as version 1.4, will want to transition to version 2.0 overall before making any additional changes needed for the much smaller transition from 2.0 to 2.1. Key documentation for the 1.x to 2.x transition:
Migrating to SQLAlchemy 2.0 - Complete background on migrating from 1.3 or 1.4 to 2.0
What’s New in SQLAlchemy 2.0? - New 2.0 features and behaviors beyond the 1.x migration
An index of all changelogs and migration documentation is at:
Changelog catalog - Detailed changelogs for all SQLAlchemy Versions