Rect#
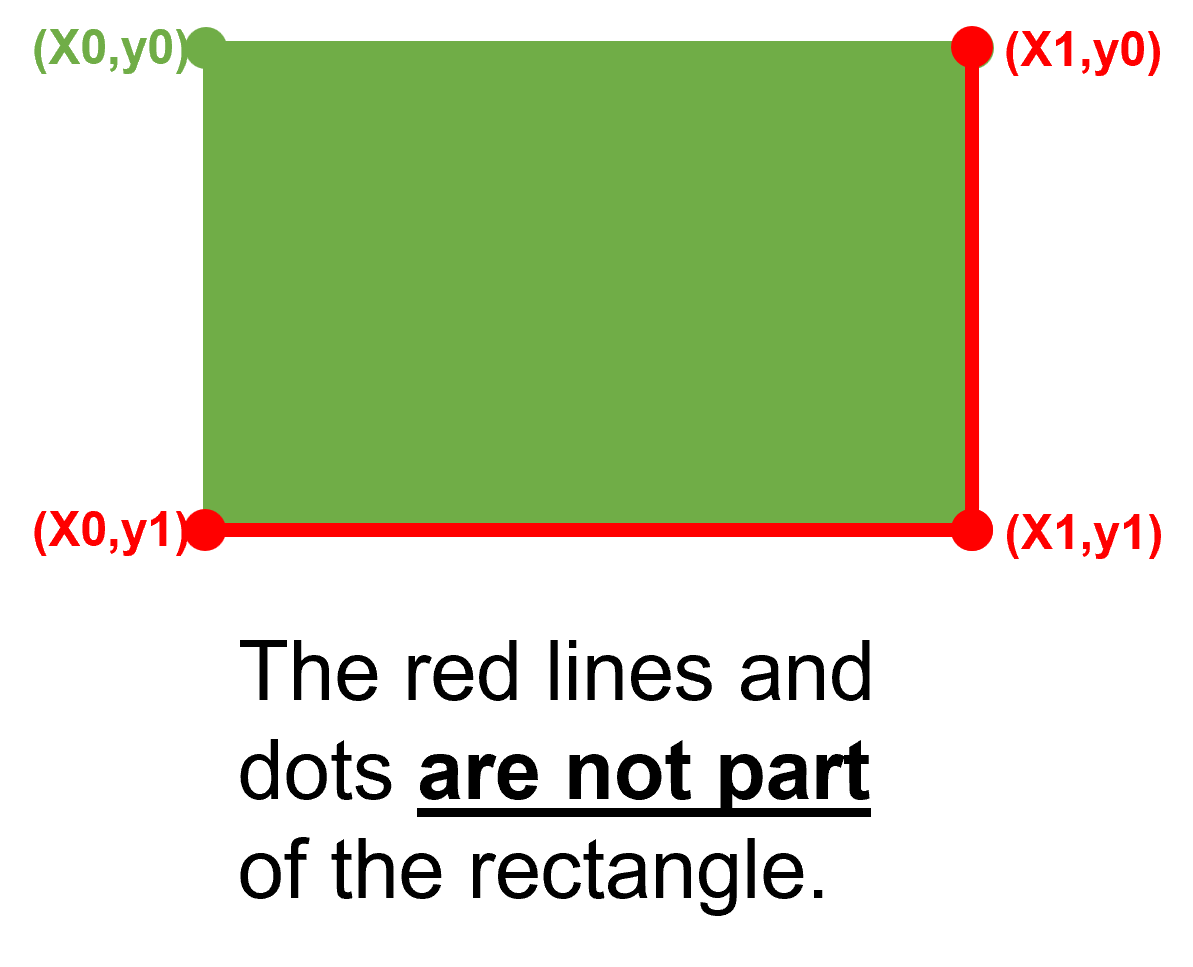
Rect 表示由四个浮动点数 x0, y0, x1, y1 定义的矩形。它们被视为两个对角线上的点的坐标。前两个数字被视为“左上”角 P(x0,y0),而 P(x1,y1) 为“右下”角。然而,这两个属性不一定与它们直观的含义相符 —— 请继续阅读。
以下说明对于 IRect 对象同样适用:
在 (Py-) MuPDF (和 PDF) 的意义上,矩形总是具有与 x 轴和 y 轴平行的边界。一般的正交四边形 不是矩形 —— 这与数学定义不同。
构造点可以(几乎!——见下文)位于平面中的任何位置 —— 它们不必不同,例如“左上”角也不一定是几何学上的“西北”点。
单位为点,其中 72 个点等于 1 英寸。
- 对于任何给定的四个数字,可以通过四种不同的方式定义几何上“相同”的矩形:
Rect(P(x0,y0), P(x1,y1))
Rect(P(x1,y1), P(x0,y0))
Rect(P(x0,y1), P(x1,y0))
Rect(P(x1,y0), P(x0,y1))
(在 v1.19.0 版本中更改) 因此,做出如下分类:
如果
x0 <= x1且y0 <= y1,则矩形称为 有效 (即右下角点位于左上角点的“东南”方向),否则为 无效 。在上述四种方式中, 仅第一种 是有效的。请注意,在 MuPDF 的坐标系统中,y 轴是从 上到下 定向的。无效矩形在早期版本中称为无限矩形。如果
x0 >= x1或y0 >= y1,则矩形称为 空矩形。这意味着 无效矩形始终为空矩形。并且,如果x0 > x1(或y0 > y1),则width(或height) 设置为零。在早期版本中,矩形仅在宽度或高度为零时才为空。矩形坐标 不能超出 数值范围
FZ_MIN_INF_RECT = -2147483648至FZ_MAX_INF_RECT = 2147483520。这两个值被选择是因为它们是能够通过 C 浮动转换来存活的最小/最大的 32 位整数。在早期版本中,坐标值没有限制。有 唯一的一个“无限”矩形,由
x0 = y0 = FZ_MIN_INF_RECT和x1 = y1 = FZ_MAX_INF_RECT定义。它包含所有其他矩形。它主要用于技术目的 —— 例如,当一个函数调用应忽略一个形式上要求的矩形参数时。这个矩形不是空的。矩形是(半)开区间的:右边和底边(包括相应的角点)不被认为是矩形的一部分。这意味着,只有左上角
(x0, y0)能属于矩形 —— 其他三个角点永远不会属于矩形。空矩形根本不包含任何角点。
以下是更改概览。
概念 |
版本 < 1.19.0 |
版本 1.19.* |
|---|---|---|
空矩形 |
x0 = x1 或 y0 = y1 |
x0 >= x1 或 y0 >= y1 – 包括无效矩形 |
有效矩形 |
不适用 |
x0 <= x1 且 y0 <= y1 |
无限矩形 |
所有 x0 > x1 或 y1 > y0 的矩形 |
仅有一个无限矩形 / irect! |
坐标值 |
所有数字 |
|
边界, 角点 |
是矩形的一部分 |
右边和底边的角点和边界 不在矩形内 |
有新的顶级函数定义了无限矩形和标准空矩形以及四边形,请参见
INFINITE_RECT()及其相关函数。
方法 / 属性 |
简要描述 |
|---|---|
检查点或矩形是否包含在矩形内 |
|
|
计算矩形面积 |
|
扩展矩形以包含一个点 |
扩展矩形以包含另一个矩形 |
|
计算与另一个矩形的公共部分 |
|
|
检查是否存在非空交集 |
|
使用点和矩阵变换矩形 |
|
转换为另一个矩形的矩阵 |
欧几里得范数 |
|
|
使矩形有效 |
创建最小的 IRect 包含矩形 |
|
使用矩阵变换矩形 |
|
|
左下角点,别名 bl |
|
右下角点,别名 br |
|
矩形高度 |
|
等于方法 round() 的结果 |
矩形是否为空 |
|
矩形是否有效 |
|
矩形是否是无限矩形 |
|
|
左上角点,别名 tl |
|
右上角点,别名 tr |
|
由矩形角点构成的 Quad |
|
矩形宽度 |
|
左角点的 x 坐标 |
|
右角点的 x 坐标 |
|
上角点的 y 坐标 |
|
下角点的 y 坐标 |
类 API
- class Rect#
- __init__(self)#
- __init__(self, x0, y0, x1, y1)#
- __init__(self, top_left, bottom_right)#
- __init__(self, top_left, x1, y1)#
- __init__(self, x0, y0, bottom_right)#
- __init__(self, rect)#
- __init__(self, sequence)#
重载构造函数:top_left、bottom_right 代表
point_like对象,”sequence” 是一个包含 4 个数字的 Python 序列类型(见 在 PyMuPDF 中使用 Python 序列作为参数),”rect” 表示另一个rect_like对象,而其他参数代表坐标。如果指定了 “rect”,则构造函数会创建它的 新副本。
如果没有参数,则创建空矩形 Rect(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0)。
- round()#
创建最小的包含 IRect。这 不是 简单地四舍五入矩形的边:左上角向上和向左四舍五入,而右下角向下和向右四舍五入。
>>> pymupdf.Rect(0.5, -0.01, 123.88, 455.123456).round() IRect(0, -1, 124, 456)
如果矩形 为空,结果也为空。
可能的悖论: 即使矩形 不 为空,结果也可能为空!在这种情况下,结果显然不包含该矩形。因为 MuPDF 的算法允许有一个小的公差(1e-3)。示例:
>>> r = pymupdf.Rect(100, 100, 200, 100.001) >>> r.is_empty # 矩形 **不是** 空的 False >>> r.round() # 但是它的 irect 是空的! pymupdf.IRect(100, 100, 200, 100) >>> r.round().is_empty True
- 返回类型:
- transform(m)#
使用矩阵变换矩形并 替换原始矩形。如果矩形为空或无限,则不进行任何操作。
- 参数:
m (Matrix) – 变换矩阵。
- 返回类型:
Rect
- 返回:
包含变换后的矩形的最小矩形。
- norm()#
计算矩形的欧几里得范数。
- 返回类型:
float
- 返回:
欧几里得范数,即矩形的对角线长度。
- is_infinite()#
检查矩形是否是“无限矩形”。
- 返回类型:
bool
- 返回:
如果矩形是无限的,则返回
True,否则返回False。
- is_empty()#
检查矩形是否为空。
- 返回类型:
bool
- 返回:
如果矩形为空,则返回
True,否则返回False。
- is_valid()#
检查矩形是否有效(即其左上角坐标小于右下角坐标)。
- 返回类型:
bool
- 返回:
如果矩形有效,则返回
True,否则返回False。
Rect represents a rectangle defined by four floating point numbers x0, y0, x1, y1. They are treated as being coordinates of two diagonally opposite points. The first two numbers are regarded as the “top left” corner P(x0,y0) and P(x1,y1) as the “bottom right” one. However, these two properties need not coincide with their intuitive meanings – read on.
The following remarks are also valid for IRect objects:
A rectangle in the sense of (Py-) MuPDF (and PDF) always has borders parallel to the x- resp. y-axis. A general orthogonal tetragon is not a rectangle – in contrast to the mathematical definition.
The constructing points can be (almost! – see below) anywhere in the plane – they need not even be different, and e.g. “top left” need not be the geometrical “north-western” point.
Units are in points, where 72 points is 1 inch.
- For any given quadruple of numbers, the geometrically “same” rectangle can be defined in four different ways:
Rect(P(x0,y0), P(x1,y1))
Rect(P(x1,y1), P(x0,y0))
Rect(P(x0,y1), P(x1,y0))
Rect(P(x1,y0), P(x0,y1))
(Changed in v1.19.0) Hence some classification:
A rectangle is called valid if
x0 <= x1andy0 <= y1(i.e. the bottom right point is “south-eastern” to the top left one), otherwise invalid. Of the four alternatives above, only the first is valid. Please take into account, that in MuPDF’s coordinate system, the y-axis is oriented from top to bottom. Invalid rectangles have been called infinite in earlier versions.A rectangle is called empty if
x0 >= x1ory0 >= y1. This implies, that invalid rectangles are also always empty. Andwidth(resp.height) is set to zero ifx0 > x1(resp.y0 > y1). In previous versions, a rectangle was empty only if one of width or height was zero.Rectangle coordinates cannot be outside the number range from
FZ_MIN_INF_RECT = -2147483648toFZ_MAX_INF_RECT = 2147483520. Both values have been chosen, because they are the smallest / largest 32bit integers that survive C float conversion roundtrips. In previous versions there was no limit for coordinate values.There is exactly one “infinite” rectangle, defined by
x0 = y0 = FZ_MIN_INF_RECTandx1 = y1 = FZ_MAX_INF_RECT. It contains every other rectangle. It is mainly used for technical purposes – e.g. when a function call should ignore a formally required rectangle argument. This rectangle is not empty.Rectangles are (semi-) open: The right and the bottom edges (including the resp. corners) are not considered part of the rectangle. This implies, that only the top-left corner
(x0, y0)can ever belong to the rectangle - the other three corners never do. An empty rectangle contains no corners at all.

Here is an overview of the changes.
Notion |
Versions < 1.19.0 |
Versions 1.19.* |
|---|---|---|
empty |
x0 = x1 or y0 = y1 |
x0 >= x1 or y0 >= y1 – includes invalid rects |
valid |
n/a |
x0 <= x1 and y0 <= y1 |
infinite |
all rects where x0 > x1 or y1 > y0 |
exactly one infinite rect / irect! |
coordinate values |
all numbers |
|
borders, corners |
are parts of the rectangle |
right and bottom corners and edges are outside |
There are new top level functions defining infinite and standard empty rectangles and quads, see
INFINITE_RECT()and friends.
Methods / Attributes |
Short Description |
|---|---|
checks containment of point_likes and rect_likes |
|
|
calculate rectangle area |
|
enlarge rectangle to also contain a point |
enlarge rectangle to also contain another one |
|
common part with another rectangle |
|
|
checks for non-empty intersections |
|
transform with a point and a matrix |
|
the matrix that transforms to another rectangle |
the Euclidean norm |
|
|
makes a rectangle valid |
create smallest IRect containing rectangle |
|
transform rectangle with a matrix |
|
|
bottom left point, synonym bl |
|
bottom right point, synonym br |
|
rectangle height |
|
equals result of method round() |
whether rectangle is empty |
|
whether rectangle is valid |
|
whether rectangle is infinite |
|
|
top left point, synonym tl |
|
top_right point, synonym tr |
|
Quad made from rectangle corners |
|
rectangle width |
|
left corners’ x coordinate |
|
right corners’ x -coordinate |
|
top corners’ y coordinate |
|
bottom corners’ y coordinate |
Class API
备注
This class adheres to the Python sequence protocol, so components can be accessed via their index, too. Also refer to 在 PyMuPDF 中使用 Python 序列作为参数.
Rectangles can be used with arithmetic operators – see chapter 几何对象的运算符代数.