Wireshark 实验室#
Wireshark Lab
Wireshark 实验
“Tell me and I forget. Show me and I remember. Involve me and I understand.”
——中国谚语
通过亲眼观察网络协议的实际运行过程并亲自进行相关操作,通常可以极大地加深对网络协议的理解——例如观察两个协议实体之间交换的消息序列、深入了解协议的运行细节、引导协议执行特定动作,并观察这些动作及其结果。这些操作既可以在模拟环境中完成,也可以在真实的网络环境(如 Internet)中完成。教材网站上的 Java 小程序采用的是前一种方式;而在 Wireshark 实验中,我们将采用后一种方式。你将使用自己桌面上的、家中的或实验室中的计算机,在各种场景中运行网络应用。你将观察到你计算机中的网络协议如何与 Internet 中其他位置的协议实体进行交互和消息交换。因此,你和你的计算机将是这些实时实验的核心组成部分。你将通过实践进行观察——并由此获得学习。
用于观察正在运行的协议实体之间交换消息的基本工具称为 分组嗅探器。顾名思义,分组嗅探器以被动方式复制(嗅探)从你的计算机发送和接收的消息;它还会显示所捕获消息中各协议字段的内容。图 1.28 展示了 Wireshark 分组嗅探器的屏幕截图。Wireshark 是一款免费的分组嗅探器,支持在 Windows、Linux/Unix 和 Mac 计算机上运行。
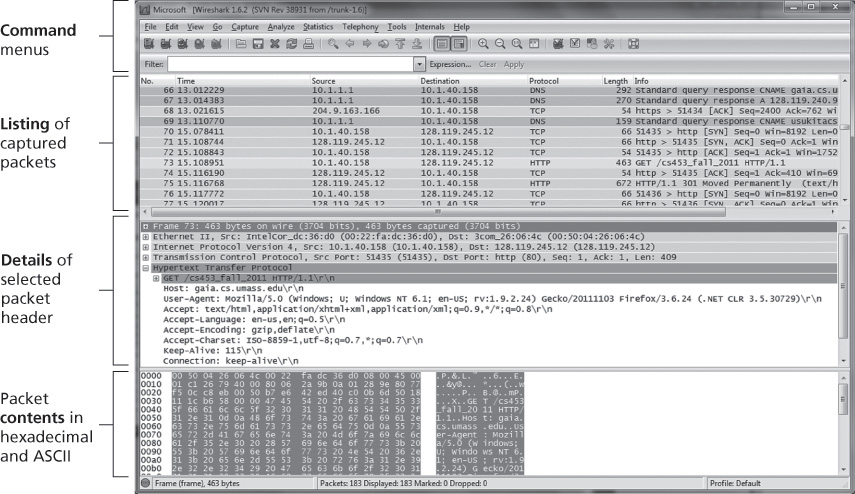
图 1.28 Wireshark 屏幕截图(由 Wireshark 基金会授权转载)
在整本教材中,你将会看到多个 Wireshark 实验,它们将帮助你探索本章学习的多种协议。在本书的第一个 Wireshark 实验中,你将获取并安装一份 Wireshark,访问一个网站,并捕获并检查你 Web 浏览器与 Web 服务器之间交换的协议消息。
关于本第一个 Wireshark 实验的完整细节(包括如何获取和安装 Wireshark 的说明)可在网站 http://www.pearsonhighered.com/cs-resources/ 上查阅。
“Tell me and I forget. Show me and I remember. Involve me and I understand.”
—Chinese proverb
One’s understanding of network protocols can often be greatly deepened by seeing them in action and by playing around with them—observing the sequence of messages exchanged between two protocol entities, delving into the details of protocol operation, causing protocols to perform certain actions, and observing these actions and their consequences. This can be done in simulated scenarios or in a real network environment such as the Internet. The Java applets at the textbook Web site take the first approach. In the Wireshark labs, we’ll take the latter approach. You’ll run network applications in various scenarios using a computer on your desk, at home, or in a lab. You’ll observe the network protocols in your computer, interacting and exchanging messages with protocol entities executing elsewhere in the Internet. Thus, you and your computer will be an integral part of these live labs. You’ll observe—and you’ll learn—by doing.
The basic tool for observing the messages exchanged between executing protocol entities is called a packet sniffer. As the name suggests, a packet sniffer passively copies (sniffs) messages being sent from and received by your computer; it also displays the contents of the various protocol fields of these captured messages. A screenshot of the Wireshark packet sniffer is shown in Figure 1.28. Wireshark is a free packet sniffer that runs on Windows, Linux/Unix, and Mac computers.

- align:
center
- name:
A Wireshark screenshot (Wireshark screenshot reprinted by permission of the Wireshark Foundation.)
Figure 1.28 A Wireshark screenshot (Wireshark screenshot reprinted by permission of the Wireshark Foundation.)
Throughout the textbook, you will find Wireshark labs that allow you to explore a number of the protocols studied in the chapter. In this first Wireshark lab, you’ll obtain and install a copy of Wireshark, access a Web site, and capture and examine the protocol messages being exchanged between your Web browser and the Web server.
You can find full details about this first Wireshark lab (including instructions about how to obtain and install Wireshark) at the Web site http://www.pearsonhighered.com/cs-resources/.